Unveiling the secrets of blood composition, blood hematocrit virtual lab answers provide an immersive learning experience. Embark on a journey into the realm of hematology, where we unravel the significance of hematocrit levels, explore the intricacies of virtual lab simulations, and delve into case studies to unravel the mysteries of blood-related conditions.
Through a captivating narrative, this guide empowers you to grasp the fundamentals of hematocrit measurement, analyze data, and interpret results with precision. Step into the virtual laboratory and witness the transformative power of interactive learning as you navigate through the complexities of blood hematocrit.
Blood Hematocrit
The hematocrit is a measure of the volume of red blood cells (RBCs) in a given volume of blood. It is expressed as a percentage or fraction of the total blood volume occupied by RBCs. The hematocrit is a significant indicator of overall health and can provide valuable insights into various physiological processes.
Factors Influencing Hematocrit Levels
Several factors can influence hematocrit levels, including:
- Age:Hematocrit levels are generally higher in males than in females and tend to decrease with age.
- Altitude:Individuals living at higher altitudes typically have higher hematocrit levels due to increased red blood cell production in response to lower oxygen availability.
- Hydration Status:Dehydration can lead to an increase in hematocrit as the plasma volume decreases, resulting in a higher concentration of RBCs.
- Physiological Conditions:Certain medical conditions, such as anemia and polycythemia, can significantly affect hematocrit levels.
- Medications:Some medications, such as corticosteroids and diuretics, can alter hematocrit levels.
Clinical Implications of Hematocrit Levels:
- Anemia:Hematocrit levels below the normal range may indicate anemia, a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin.
- Polycythemia:Hematocrit levels above the normal range may suggest polycythemia, a condition in which the blood has an abnormally high concentration of red blood cells.
- Dehydration:Elevated hematocrit levels can be a sign of dehydration, indicating the need for increased fluid intake.
- Monitoring Treatment:Hematocrit levels are closely monitored during certain medical treatments, such as blood transfusions and chemotherapy, to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
Virtual Lab Simulation: Blood Hematocrit Virtual Lab Answers
Understanding Hematocrit Measurement, Blood hematocrit virtual lab answers
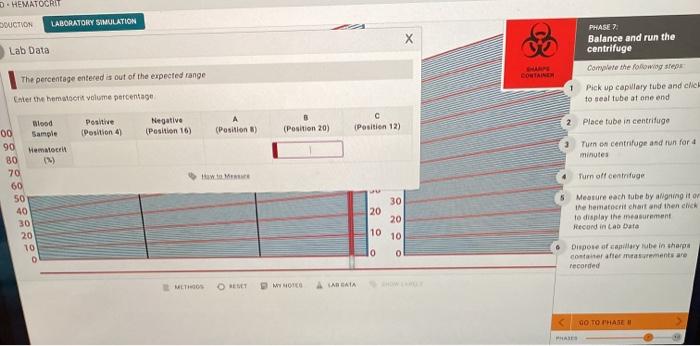
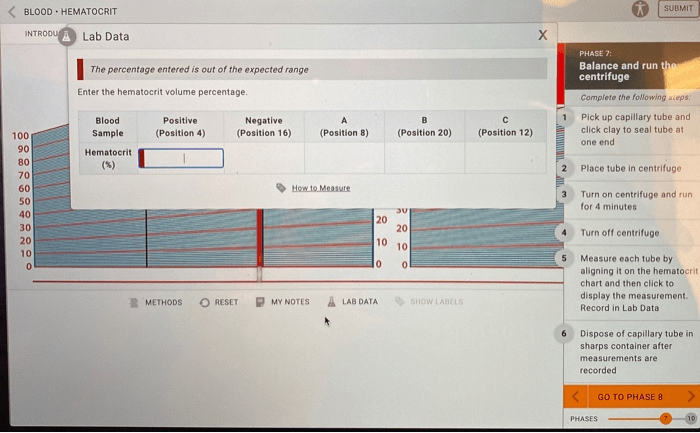
The virtual lab simulation for hematocrit measurement provides an interactive environment to explore the principles and procedures involved in determining the hematocrit level. It allows users to simulate the process of preparing a blood sample, centrifuging it, and measuring the packed cell volume to calculate the hematocrit.
Steps of the Simulation
The simulation guides users through the following steps:
- Sample Preparation:Users collect a blood sample and place it in a microhematocrit capillary tube.
- Centrifugation:The capillary tube is placed in a centrifuge and spun at high speed to separate the blood cells from the plasma.
- Packed Cell Volume Measurement:After centrifugation, the capillary tube is removed, and the length of the packed red blood cells (hematocrit) is measured using a hematocrit reader.
- Hematocrit Calculation:The hematocrit is calculated as the ratio of the packed cell volume to the total blood volume in the capillary tube.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
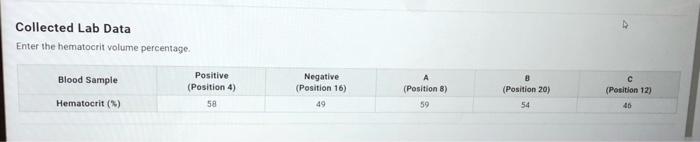
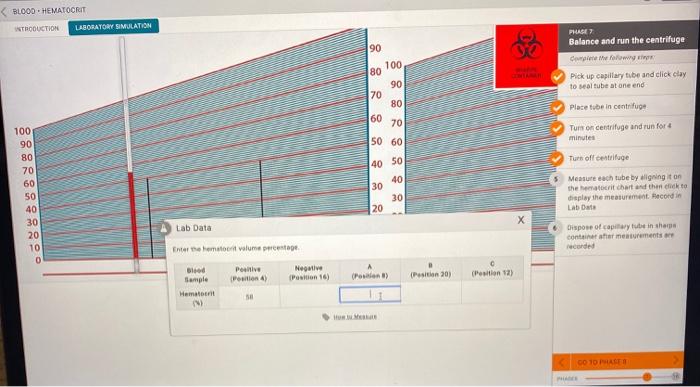
The data obtained from the virtual lab simulation can be analyzed to determine the hematocrit value, which is the percentage of red blood cells in the blood. Hematocrit is an important indicator of overall health, as it can provide insights into conditions such as anemia, dehydration, or polycythemia.
To calculate the hematocrit value, the following steps can be taken:
- Measure the height of the red blood cell column (hRBC) in millimeters.
- Measure the height of the total blood column (hTotal) in millimeters.
- Calculate the hematocrit value using the formula: Hematocrit (%) = (hRBC / hTotal) x 100
The normal range for hematocrit values varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and altitude. However, typical ranges are:
- Men: 40-54%
- Women: 36-48%
- Children: 32-44%
Interpreting the results of the hematocrit test involves comparing the obtained value to the normal ranges. Values below the normal range may indicate anemia, while values above the normal range may indicate dehydration or polycythemia.
Sources of Error
There are several potential sources of error that can affect the accuracy of the hematocrit test. These include:
- Improper sample collection:If the blood sample is not collected properly, it may contain air bubbles or other contaminants that can affect the results.
- Incorrect measurement of the blood column heights:If the heights of the red blood cell column and the total blood column are not measured accurately, the calculated hematocrit value will be incorrect.
- Variations in hematocrit levels:Hematocrit levels can vary throughout the day and from day to day. This can lead to variability in the results of the test.
To minimize the impact of these sources of error, it is important to follow the instructions for the virtual lab simulation carefully and to ensure that the measurements are taken accurately.
Case Study: Hematocrit Abnormalities
Individuals may present with abnormal hematocrit levels, either elevated (polycythemia) or decreased (anemia). These abnormalities can stem from various underlying causes, ranging from physiological adaptations to pathological conditions.
Identifying the cause of hematocrit abnormalities involves a systematic approach, considering the patient’s medical history, physical examination findings, and laboratory investigations. A thorough assessment is essential to guide appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
Elevated Hematocrit (Polycythemia)
Elevated hematocrit levels, also known as polycythemia, can result from:
- Physiological adaptations, such as high-altitude living or strenuous exercise
- Increased red blood cell production, as seen in conditions like polycythemia vera
- Decreased plasma volume, leading to hemoconcentration
Diagnostic tests may include a complete blood count, bone marrow aspiration, and genetic analysis to differentiate between these causes.
Decreased Hematocrit (Anemia)
Decreased hematocrit levels, or anemia, can arise from:
- Insufficient red blood cell production, as in iron deficiency anemia or aplastic anemia
- Increased red blood cell destruction, as in hemolytic anemia
- Blood loss, such as from trauma or gastrointestinal bleeding
Diagnosis involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and laboratory investigations, including blood tests, reticulocyte count, and stool analysis for occult blood.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of hematocrit levels?
Hematocrit levels provide valuable insights into the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood, helping diagnose conditions such as anemia and dehydration.
How does the virtual lab simulation enhance hematocrit measurement learning?
The virtual lab simulation offers a safe and interactive environment to practice sample preparation, data collection, and analysis, fostering a deeper understanding of hematocrit measurement techniques.
What are the potential sources of error in hematocrit measurement?
Errors can arise from improper sample collection, inadequate centrifugation, or incorrect data interpretation, emphasizing the importance of following standardized protocols.