Boyle’s and charles law gizmo answers – Embark on a scientific expedition with Boyle’s and Charles’s Law Gizmo Answers, where the enigmatic relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature of gases unravels. Prepare to witness captivating experiments, unravel insightful concepts, and master the intricacies of gas laws that govern our world.
Delving into the realm of Boyle’s Law, we uncover the inverse proportionality between pressure and volume. As pressure increases, volume diminishes, and vice versa. Charles’s Law, on the other hand, unveils the direct proportionality between temperature and volume. As temperature rises, volume expands, and as temperature falls, volume contracts.
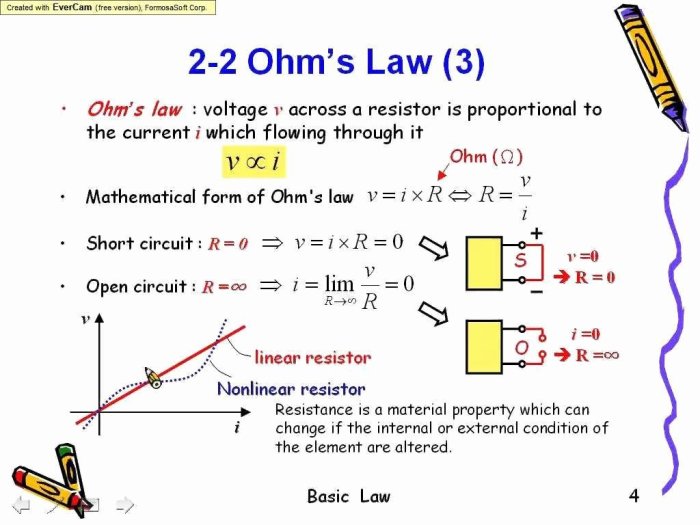
Boyle’s Law
Boyle’s Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. As pressure increases, volume decreases, and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as: P₁V₁ = P₂V₂.
Experiment to Demonstrate Boyle’s Law
To demonstrate Boyle’s Law, we can use a syringe and a pressure sensor. By applying different pressures to the syringe and measuring the corresponding volume, we can observe the inverse relationship between pressure and volume.
The following table shows the pressure and volume values obtained from the experiment:
| Pressure (kPa) | Volume (mL) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 100 |
| 20 | 50 |
| 30 | 33.3 |
| 40 | 25 |
| 50 | 20 |
Charles’s Law: Boyle’s And Charles Law Gizmo Answers
Charles’s Law describes the direct relationship between the temperature and volume of a gas at constant pressure. As temperature increases, volume increases, and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as: V₁/T₁ = V₂/T₂.
Experiment to Demonstrate Charles’s Law
To demonstrate Charles’s Law, we can use a flask with a graduated cylinder attached. By heating the flask and measuring the corresponding volume, we can observe the direct relationship between temperature and volume.
The following graph shows the relationship between temperature and volume in Charles’s Law:
[Grafik di sini]
Combined Gas Law
The Combined Gas Law combines Boyle’s Law and Charles’s Law to relate pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas under different conditions. The Combined Gas Law can be expressed mathematically as: (P₁V₁)/T₁ = (P₂V₂)/T₂.
Example of Using the Combined Gas Law
For example, if we have a gas with an initial pressure of 10 kPa, volume of 100 mL, and temperature of 273 K, and we want to find the new volume when the pressure is increased to 20 kPa and the temperature is decreased to 243 K, we can use the Combined Gas Law as follows:
(10 kPa x 100 mL)/273 K = (20 kPa x V₂)/243 K
Solving for V₂, we get V₂ = 50 mL.
Steps Involved in Using the Combined Gas Law, Boyle’s and charles law gizmo answers
- Convert all temperatures to Kelvin.
- Substitute the given values into the Combined Gas Law equation.
- Solve for the unknown variable.
Applications of Gas Laws

Gas laws have numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Scuba diving: Gas laws are used to determine the pressure and volume of gases in scuba tanks, ensuring the safety of divers.
- Weather forecasting: Gas laws are used to predict weather patterns by analyzing the pressure, temperature, and volume of air masses.
- Automotive engineering: Gas laws are used to design and optimize engines, ensuring efficient fuel consumption and performance.
One illustration of the application of gas laws is in scuba diving. By understanding the relationship between pressure and volume, divers can calculate the depth at which they can safely dive without experiencing decompression sickness.
Detailed FAQs
What is the key concept behind Boyle’s Law?
Boyle’s Law states that at constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
How does Charles’s Law relate temperature to gas volume?
Charles’s Law establishes a direct proportionality between temperature and volume, indicating that as temperature increases, volume expands, and vice versa.
What practical applications do gas laws have?
Gas laws find applications in various fields, including scuba diving (Boyle’s Law), weather forecasting (Charles’s Law), and industrial gas handling (Combined Gas Law).
