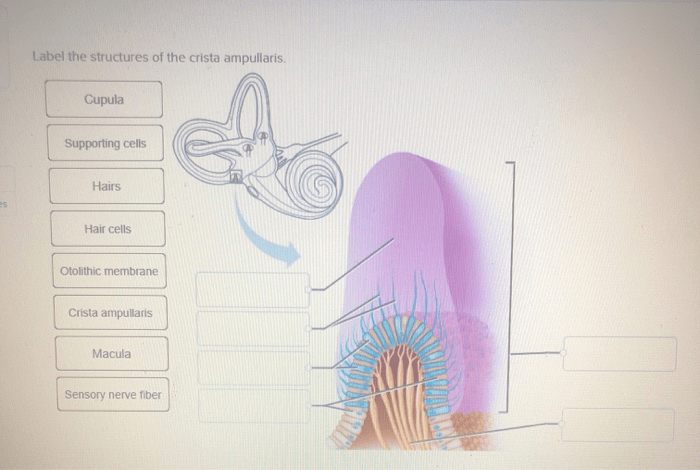
Label the structures of the crista ampullaris. – The crista ampullaris, a crucial component of the vestibular system, plays a vital role in maintaining balance and equilibrium. This complex structure, located within the inner ear, is responsible for detecting angular acceleration of the head and transmitting this information to the brain.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of the crista ampullaris, providing a comprehensive understanding of its essential role in maintaining our sense of balance.
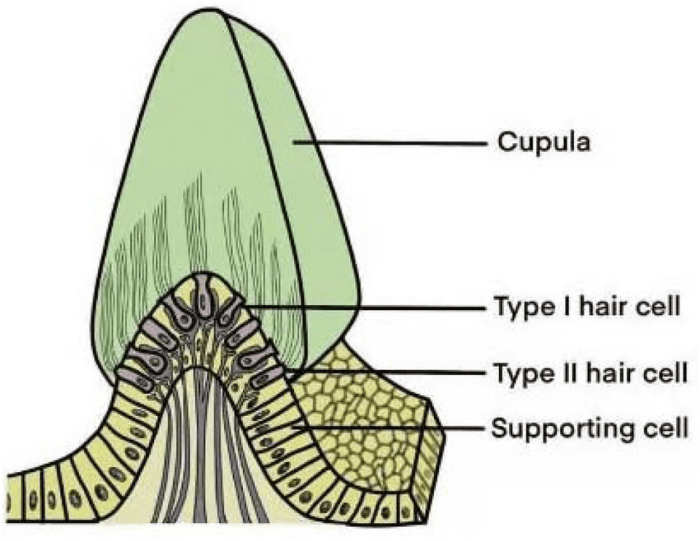
The crista ampullaris consists of sensory cells, known as hair cells, which are embedded within a gelatinous structure called the cupula. When the head rotates, the cupula moves, bending the hair cells and triggering a neural response. This response is then transmitted to the brain via the vestibular nerve, providing information about the direction and velocity of head movement.
Introduction: Label The Structures Of The Crista Ampullaris.
The crista ampullaris is a sensory structure located in the inner ear that plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and equilibrium. It is responsible for detecting angular acceleration of the head, which is essential for maintaining spatial orientation and coordinating movement.
The crista ampullaris is composed of a group of sensory cells, known as hair cells, which are embedded in a gelatinous substance called the cupula. The cupula is attached to the roof of the ampulla, a fluid-filled cavity within the semicircular canal.
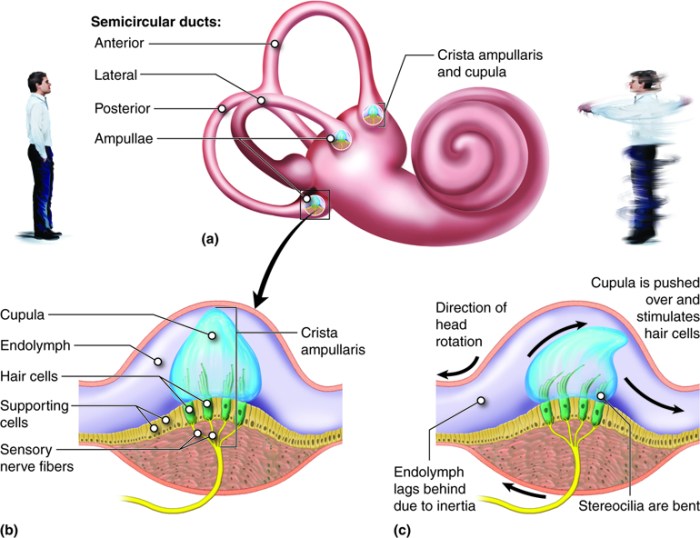
When the head rotates, the fluid in the canal moves, causing the cupula to bend. This bending stimulates the hair cells, which then transmit signals to the brain via the vestibular nerve.
Components of the Crista Ampullaris
The crista ampullaris is composed of the following components:
- Sensory cells (hair cells):The hair cells are the sensory receptors of the crista ampullaris. They are arranged in rows and have a cluster of stereocilia, which are hair-like projections that extend into the cupula.
- Cupula:The cupula is a gelatinous substance that is attached to the roof of the ampulla. It is composed of a network of collagen fibers and glycosaminoglycans.
- Innervation:The crista ampullaris is innervated by the vestibular nerve, which transmits signals from the hair cells to the brain.
Function of the Crista Ampullaris, Label the structures of the crista ampullaris.
The crista ampullaris is responsible for detecting angular acceleration of the head. When the head rotates, the fluid in the semicircular canal moves, causing the cupula to bend. This bending stimulates the hair cells, which then transmit signals to the brain via the vestibular nerve.
The brain uses the information from the crista ampullaris to determine the direction and magnitude of head movement. This information is then used to control eye movements, maintain balance, and coordinate movement.
Clinical Significance
Damage to the crista ampullaris can lead to balance disorders, such as vertigo and dizziness. Vertigo is a sensation of spinning or whirling, while dizziness is a feeling of lightheadedness or unsteadiness.
Damage to the crista ampullaris can be caused by a variety of factors, including head injury, infection, and certain medications. Diagnostic tests, such as the Dix-Hallpike maneuver and electronystagmography (ENG), can be used to assess the function of the crista ampullaris.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the function of the crista ampullaris?
The crista ampullaris detects angular acceleration of the head, providing information about the direction and velocity of head movement.
How does the crista ampullaris detect head movement?
The crista ampullaris contains sensory cells (hair cells) embedded in a gelatinous structure called the cupula. When the head rotates, the cupula moves, bending the hair cells and triggering a neural response.
What is the clinical significance of the crista ampullaris?
Damage to the crista ampullaris can lead to balance disorders, such as dizziness and vertigo. Diagnostic tests, such as the caloric test and electronystagmography, can be used to assess the function of the crista ampullaris.