Part of the knee crossword welcomes you to a realm of cryptic clues and tantalizing puzzles. Immerse yourself in a labyrinth of words that will test your knowledge of the human body and ignite your curiosity.
Delve into the intricate anatomy of the knee, decipher the secrets of common knee injuries, and unravel the mysteries of surgical interventions. Along the way, discover the art of physical examination, explore innovative treatment options, and uncover the latest advancements in knee care.
Anatomical Structures of the Knee

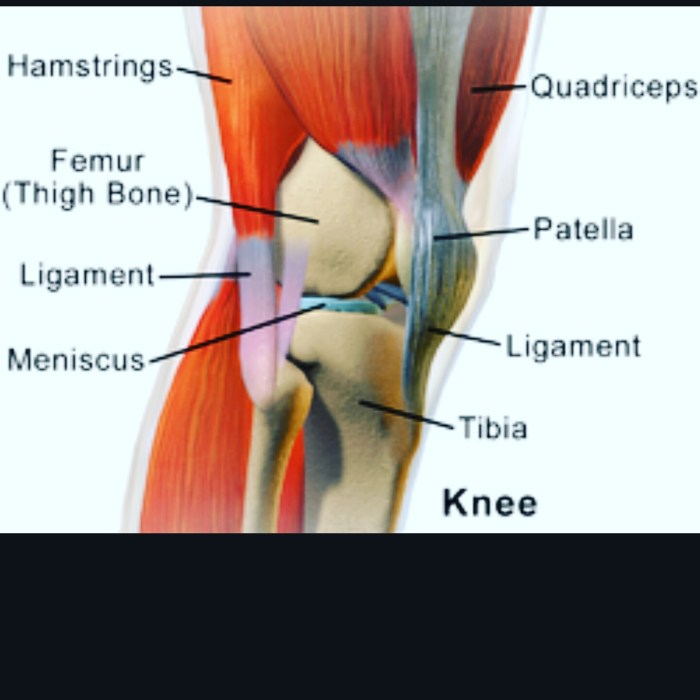
The knee is a complex joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia) and kneecap (patella). It allows for a wide range of motion, including flexion, extension, and rotation.
Bones of the Knee
- Femur (thigh bone)
- Tibia (shin bone)
- Patella (kneecap)
Ligaments of the Knee, Part of the knee crossword
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect bones together. The knee joint is supported by several ligaments, including:
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
- Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL)
- Lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
Muscles of the Knee
Muscles are responsible for moving the knee joint. The muscles that surround the knee include:
- Quadriceps
- Hamstrings
- Calf muscles
Role of the Patella
The patella, or kneecap, is a small bone that sits in front of the knee joint. It helps to protect the joint from injury and provides leverage for the quadriceps muscles.
Common Knee Injuries
The knee joint is a complex structure prone to various injuries due to its weight-bearing function and extensive mobility. Understanding the most prevalent knee injuries can help individuals identify and manage these conditions effectively.
The causes of knee injuries range from traumatic incidents, such as sports injuries or falls, to overuse and degenerative conditions. Symptoms vary depending on the specific injury, but common signs include pain, swelling, stiffness, instability, and reduced range of motion.
Part of the knee can be a puzzle in a crossword. A different type of puzzle is the dry scalp vs dandruff quiz . These quizzes can help you understand the difference between these two common scalp conditions. Back to the crossword, the part of the knee is often a four-letter word.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tear
The ACL is a major ligament that stabilizes the knee joint, preventing excessive forward movement of the shinbone. ACL tears often occur during sports activities involving sudden changes in direction or landings from jumps. Symptoms include immediate pain, swelling, instability, and difficulty walking.
Treatment for ACL tears typically involves surgical repair followed by rehabilitation to restore stability and range of motion. Prevention strategies include strengthening exercises for the knee muscles, proper warm-up before physical activities, and avoiding high-risk maneuvers.
Meniscus Tear
The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage that cushions and stabilizes the knee joint. Meniscus tears can result from both traumatic injuries and gradual wear and tear. Symptoms include pain, swelling, catching or locking of the knee, and difficulty bending or straightening the joint.
Treatment for meniscus tears depends on the severity of the injury. Minor tears may heal with rest, ice, and physical therapy. More severe tears may require surgical repair to remove or repair the damaged cartilage.
Patellar Tendonitis
Patellar tendonitis is an inflammation of the tendon that connects the kneecap to the shinbone. It commonly affects individuals involved in activities that involve repetitive jumping or running. Symptoms include pain and tenderness below the kneecap, especially during or after exercise.
Treatment for patellar tendonitis typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy can help strengthen the knee muscles and improve flexibility. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove inflamed tissue or repair the tendon.
Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
ITBS is a condition that affects the iliotibial band, a thick band of tissue that runs along the outside of the knee. It is common among runners and cyclists. Symptoms include pain on the outside of the knee, especially when bending or straightening the joint.
Treatment for ITBS involves stretching the iliotibial band, strengthening the knee muscles, and modifying activities to reduce stress on the knee. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be necessary.
Surgical Interventions for Knee Conditions: Part Of The Knee Crossword
Surgical interventions play a crucial role in addressing various knee problems. These procedures aim to alleviate pain, restore function, and improve overall knee health. Various surgical techniques are employed, each tailored to specific knee conditions and patient needs.
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a small camera and surgical instruments into the knee joint through small incisions. It allows surgeons to visualize the knee’s interior, diagnose problems, and perform necessary repairs or procedures. Arthroscopic surgery is commonly used to treat meniscus tears, ligament injuries, and cartilage damage.
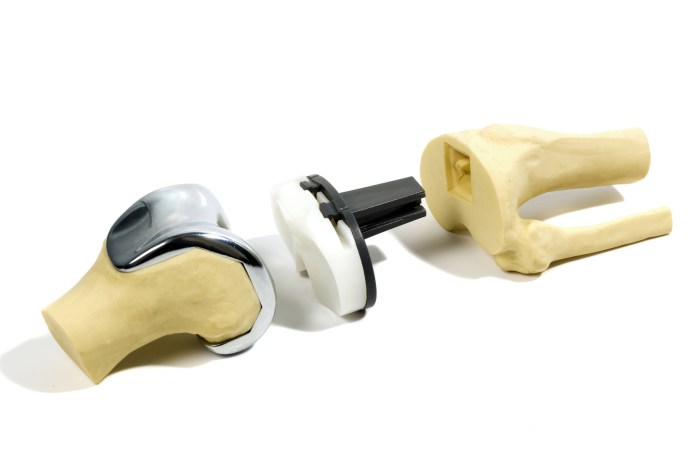
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement (TKR) is a major surgical procedure that involves replacing the damaged knee joint with an artificial implant. TKR is typically recommended for patients with severe arthritis or other conditions that have caused significant knee pain and disability.
The procedure aims to restore pain-free movement and improve the patient’s quality of life.
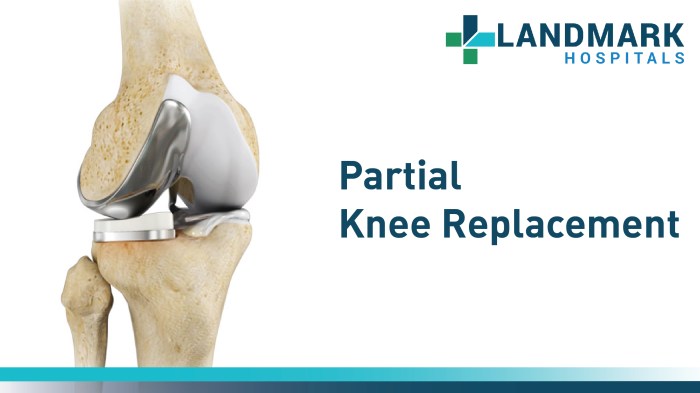
Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement (PKR) is a less invasive alternative to TKR that involves replacing only the damaged portion of the knee joint. PKR is suitable for patients with arthritis that affects only a specific compartment of the knee, such as the medial or lateral compartment.
This procedure preserves more of the natural knee joint and offers a faster recovery time compared to TKR.
Meniscus Repair
Meniscus repair is a surgical procedure that aims to repair a torn meniscus, a C-shaped cartilage that provides cushioning and stability to the knee joint. The repair involves suturing or trimming the torn meniscus to restore its function and prevent further damage.
Ligament Reconstruction
Ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure that involves repairing or replacing a torn or damaged ligament in the knee. Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect bones and provide stability to the joint. Common ligament injuries include tears of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Following knee surgery, patients typically undergo a comprehensive rehabilitation program to restore range of motion, strength, and function to the knee. The rehabilitation process may involve physical therapy, occupational therapy, and home exercises. The recovery time and specific rehabilitation protocols vary depending on the type of surgery performed and the patient’s individual condition.
Physical Examination and Diagnosis of Knee Disorders
Evaluating knee disorders involves a comprehensive physical examination and diagnostic techniques to identify the underlying cause of pain, discomfort, or functional limitations. A thorough patient history, physical examination, and imaging studies are crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Physical Examination
The physical examination of the knee begins with observation of the joint, assessing any visible deformities, swelling, or skin changes. The examiner then palpates the knee to identify areas of tenderness, warmth, or crepitus. Range of motion is tested, including flexion, extension, and rotation, to evaluate joint mobility and flexibility.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques play a vital role in diagnosing knee conditions. X-rays provide clear images of bones, revealing fractures, dislocations, or degenerative changes like osteoarthritis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers detailed cross-sectional views of soft tissues, including ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, helping identify tears, sprains, or other injuries.
Patient History
A thorough patient history is essential for understanding the nature and duration of knee symptoms. The examiner inquires about the onset of pain, its location and severity, and any associated factors like trauma or repetitive activities. Past medical history, including previous knee injuries or surgeries, is also relevant.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain

Knee pain is a common problem that can affect people of all ages. The pain can range from mild to severe and can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, and overuse. There are a number of different treatment options available for knee pain, depending on the cause and severity of the pain.Non-surgical
treatment options for knee pain include:
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to reduce pain and inflammation. Prescription pain relievers may also be necessary in some cases.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve range of motion. This can help to reduce pain and improve function.
- Injections: Injections of corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid can help to reduce pain and inflammation. These injections are typically given into the knee joint.
Lifestyle modifications can also play a role in managing knee pain. These modifications include:
- Weight loss: Losing weight can help to reduce stress on the knee joint and improve pain.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve range of motion. This can help to reduce pain and improve function.
Prevention and Management of Knee Problems

Maintaining healthy knees is crucial for overall mobility and well-being. This section explores modifiable risk factors, preventive strategies, and management techniques to keep your knees in optimal condition.
Understanding the causes and contributing factors to knee problems empowers individuals to make informed decisions and adopt proactive measures to preserve knee health.
Modifiable Risk Factors for Knee Problems
- Obesity:Excess weight exerts significant stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis and other knee issues.
- Improper Exercise Techniques:Incorrect form during physical activities can lead to excessive strain and injury to the knee structures.
- Inadequate Footwear:Wearing shoes that lack proper support or cushioning can contribute to knee pain and discomfort.
- Lack of Physical Activity:Sedentary lifestyles weaken knee muscles, making them more susceptible to injuries.
- Trauma:Direct impact or sudden movements can cause acute knee injuries, such as ligament tears or fractures.
Preventive Strategies for Knee Health
- Weight Management:Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on knee joints and lowers the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Proper Exercise Techniques:Seek guidance from qualified professionals to ensure correct form during exercise, reducing the likelihood of knee injuries.
- Appropriate Footwear:Choose shoes with adequate support, cushioning, and stability for your specific activities.
- Regular Exercise:Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen knee muscles and improve joint stability.
- Protective Gear:Use protective gear, such as knee pads, during high-impact activities to minimize the risk of injuries.
Role of Nutrition and Weight Management in Knee Health
- Healthy Diet:Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for knee joint health.
- Supplements:In some cases, supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin may support joint health and reduce pain.
- Weight Loss:If overweight or obese, gradual weight loss can significantly reduce stress on knee joints and improve overall knee function.
Innovations in Knee Care
Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in the field of knee care, leading to improved surgical techniques, rehabilitation protocols, and pain management strategies. These innovations have revolutionized knee care, offering potential benefits and applications in enhancing patient outcomes.
Surgical Advancements
Minimally invasive arthroscopic techniques have gained prominence, allowing surgeons to perform procedures through small incisions, minimizing tissue damage and reducing recovery time. Robotic-assisted surgery offers greater precision and control, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with increased accuracy and efficiency.
3D-printed implants, customized to each patient’s anatomy, provide a more precise fit and improved outcomes.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the largest bone in the knee?
Femur
What is the most common type of knee injury?
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear
What is the name of the kneecap?
Patella
What is the purpose of the meniscus?
To cushion and stabilize the knee joint
What is the difference between a sprain and a strain?
A sprain is a ligament injury, while a strain is a muscle or tendon injury